Class loaders
29 January 2014
In Java, every class needs to be loaded before it can be used.
The class loader (which is part of JVM) is responsible for finding and loading the java classes.
A class loading is made once, at its first use.
Classes are uniquely identified by their fully qualified name and by the class loader which loaded them.
Popular exceptions caused by the class loading: ClassNotFoundException,
ClassCastException, NoClassDefFoundError.
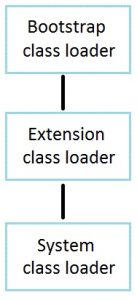
Default class loaders hierarchy of the JVM
- Bootstrap class loader
- Extensions class loader
- System class loader
Bootstrap class loader
- loads the core java libraries located in
<JAVA_HOME>/jre/lib - is written in native code
Extensions class loader
- loads the java libraries located in
<JAVA_HOME>/jre/lib/ext, or any other directory specified by thejava.ext.dirssystem property
System class loader
- loads classes found on system property
java.class.path(which by default is the current directory; you can change the value by using the-classpathor-cpcommand-line options, or setting theCLASSPATHenvironment variable. The command-line options override the setting of theCLASSPATHenvironment variable)
* Tomcat ignores this rule (see http://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-7 .0-doc/class-loader-howto.html)
Parent delegation model
Each class loader has a "parent" class loader (besides the bootstrap class loader which is the root). When creating a class loader, if there isn't specified its parent, the system class loader will become its parent class loader.
When loading a class, theClassLoader does the next actions:
- If a class has already been loaded, it returns it (from cache)
- Otherwise, it delegates the search for the new class to the parent class loader (to avoid loading
the same class multiple times which causes
ClassCastException) - If the parent class loader does not find the class,
loadClassmethod callsfindClassmethod in order to find and load the class
Role of the Thread context ClassLoader and how it can be used
Let's take some examples.
First example. Logging
Bootstrap class loader loads the java libraries (located in jre/lib) =>java.util.logging.Logger is loaded by Bootstrap class loader.
This logger
can use internationalization.
The resource bundle to be used is loaded by the System class loader.
The Bootstrap class
loader is not able to load the resource bundle, so the Logger class needs
to use the class loader of the application; more precisely, the class loader of the current thread:
ClassLoader cl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
A second example. Spring
Spring is used for managing beans. Let's say that Spring library is kept under tomcat/lib.
Those classes are loaded by the common tomcat class loader.
For each web application in webapp folder, a new class loader is created. This
class loader loads the classes in WEB-INF/classes and
WEB-INF/lib.
=> Normally, Spring cannot see those classes because they were loaded by a
different class loader.
In order to solve those issues, Java introduced the
Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader() which can get the application's class loader and
use it for loading the classes in WEB-INF/classes or
WEB-INF/lib.
Loading, Linking and Initialization of classes
Java Language Specification, Execution chapter is one of the best materials to read for this subject: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/specs/jls/se7/html/jls-12.html
References:
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Java_Classloader
- http://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/ext/basics/load.html
- http://www.onjava.com/pub/a/onjava/2004/06/30/classloader2.html
- http://www.javaworld.com/javaworld/jw-10-1996/jw-10-indepth.html
- http://tech-tauk.blogspot.ro/2009/08/thread-context-classloader-buddy.html
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/1771679/difference-between-threads-context-class-loader-and-normal-classloader